Sidebar
 This version is outdated by a newer approved version.
This version is outdated by a newer approved version. This version (2020/08/13 12:18) was approved by fschoenfeld.The Previously approved version (2020/08/05 17:14) is available.
This version (2020/08/13 12:18) was approved by fschoenfeld.The Previously approved version (2020/08/05 17:14) is available.
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Overview
ISAC (Iterative Stable Alignment and Clustering) is a 2D classification algorithm. It sorts a given stack of cryo-EM particles into different classes that share the same view of a target protein. ISAC is based around iterations of alternating equal size k-means clustering and repeated 2D alignment routines.
Yang, Z., Fang, J., Chittuluru, J., Asturias, F. J. and Penczek, P. A. (2012) Iterative stable alignment and clustering of 2D transmission electron microscope images. Structure 20, 237–247.
ISAC versions
- ISAC is the initial version as described in the original paper. At this point this implementation is obsolete and has been replaced by ISAC2 and GPU ISAC (see below).
- ISAC2 is an improved version of ISAC and used by default tool to produce 2D class averages in the SPHIRE (git) software package and the TranSPHIRE automated pipeline for processing cryo-EM data. ISAC2 is a CPU-only implementation and was developed to run on a computer cluster.
- GPU ISAC was developed to run ISAC2 on a single workstation by outsourcing its computationally expensive bottleneck calculations to any available GPUs, while simultaneously keeping its MPI-based CPU parallelization otherwise intact. GPU ISAC is currently only provided as an add-on to SPHIRE that can be installed manually (see below).
Download & Installation
- CUDA: These installation instructions assume that CUDA is already installed on your system. You can confirm this by running
nvcc --versionin your terminal; the resulting output should list the version of your installed CUDA compilation tools.
- SPHIRE: In order to use GPU ISAC, SPHIRE needs to be installed. You can find the SPHIRE download and installation instructions here. You can confirm a working SPHIRE version by running
which sphirein your terminal; the resulting output should give you the path to your SPHIRE installation (the path should indicate a version number of 1.3 or higher).
Download
- GPU ISAC is currently developed as a manually installed add-on for SPHIRE and distributed as a .zip file that can be found here: GPU ISAC download link.
Installation
Before you start, make sure your SPHIRE environment is activated.
How to activate your SPHIRE environment:
How to activate your SPHIRE environment:
- During the SPHIRE installation, an Anaconda environment for SPHIRE was created. You can list your available Anaconda environments using:
conda env list
- Look for your SPHIRE environment and activate it using either:
conda activate NAME_OF_YOUR_ENVIRONMENT
or
source activate NAME_OF_YOUR_ENVIRONMENT
It will depend on your system and Anaconda installation which one of these you will have to use.
GPU ISAC comes with a handy installation script that can be used as follows:
- Extract the archive to your chosen GPU ISAC installation folder.
- Open a terminal and navigate to your installation folder.
- Run the installation script:
./install.sh
All done!
Running GPU ISAC
An example call to use GPU ISAC looks as follows:
mpirun /path/to/sxisac2_gpu.py bdb:path/to/stack path/to/output --CTF -–radius=160 --target_radius=29 --target_nx=76 --img_per_grp=100 --minimum_grp_size=60 --thld_err=0.7 --center_method=0 --gpu_devices=0,1
Using the following mix of both mandatory and optional parameters (see below to learn which is which):
mpirun /path/to/sxisac2_gpu.py bdb:path/to/stack path/to/output --CTF -–radius=160 --target_radius=29 --target_nx=76 --img_per_grp=100 --minimum_grp_size=60 --thld_err=0.7 --center_method=0 --gpu_devices=0,1
[ ! ] - Mandatory parameters in the GPU ISAC call:
mpirunis not a GPU ISAC parameter, but is required to launch GPU ISAC using MPI parallelization (GPU ISAC uses both CPU/MPI and GPU/CUDA parallelization)./path/to/sxisac2_gpu.pyis the path to your sxisac2_gpu.py file. If you followed these instructions it should beyour/installation/path/gpu_isac_2.2/bin/sxisac2_gpu.py.path/to/stackis the path to your input .bdb stack. If you prefer to use an .hdf stack, simply remove thebdb:prefix.path/to/outputis the path to your preferred output directory.--radius=160is the radius of your target particle (in pixels) and has to be set accordingly.
[?] - Optional parameters in the GPU ISAC call:
- Using
--gpu_devicesyou can set what GPUs to use. This example uses two GPUs with id values 0 and 1, respectively. You can check the id values of your available GPUs by executingnvidia-smiin your terminal (GPUs are sorted by capability, with 0 being your strongest GPU). - You can also use
--img_per_grpto limit the maximum size of individual classes. Empirically, a class size of 100-200 (30-50 for negative stain) particles has been proven successful when dealing with around 100,000 particles. - Similarly, you can also use
--minimum_grp_sizeto limit the minimum size of individual classes. In general, this value should be around 50-60% of your maximum class size.
- The full list of GPU ISAC / ISAC2 parameters can be found here.
- Additional utilities that are helpful when using any version of ISAC can be found here.
- More information about using ISAC for 2D classification can also be found in the ISAC chapter of the official SPHIRE tutorial (link to .pdf file).
Examples
EXAMPLE 01: Test run
This example is a test run that can be used to confirm GPU ISAC was installed successfully. It is a small stack that contains 64 artificial faces and is already included in the GPU ISAC installation package. You can process it using GPU ISAC as follows:
- In your terminal, navigate to your GPU ISAC installation folder:
cd /gpu/isac/installation/folder
- Run GPU ISAC:
mpirun bin/sxisac2_gpu.py 'bdb:examples/isac_dummy_data_64#faces' 'isac_out_test/' --radius=32 --img_per_grp=8 --minimum_grp_size=4 --gpu_devices=0
Note that we don't care about the quality of any produced averages here; this test is used to make sure there are no runtime issues before a more time consuming run is executed.
EXAMPLE 02: TcdA1 toxin data
This example uses the SPHIRE tutorial data set (link to .tar file) described in the SPHIRE tutorial (link to .pdf file). The data contains about 10,000 particles from 112 micrographs and was originally published here (Gatsogiannis et al, 2013).
After downloading the data you'll notice that the extracted folder contains a multitude of subfolders. For the purposes of this example we are only interested in the Particles/ folder that stores the original data as a .bdb file.
You can process this stack using GPU ISAC as follows:
- In your terminal, navigate to your GPU ISAC installation folder:
cd /gpu/isac/installation/folder
- Run GPU ISAC:
mpirun bin/sxisac2_gpu.py 'bdb:/your/path/to/Particles/#stack' 'isac_out_TcdA1' --radius=29 --img_per_grp=100 --minimum_grp_size=50 --center_method=0 --gpu_devices=0
- Replace
/your/path/to/Particles/with the path to theParticles/directory you just downloaded. - Optional: Replace
–gpu_devices=0with–gpu_devices=0,1if you have two GPUs available (and so on).
The final averages can then be found in isac_out_TcdA1/ordered_class_averages.hdf. You can look at them using e2display.py (or any other displaying program of your choice) and should see averages like these:
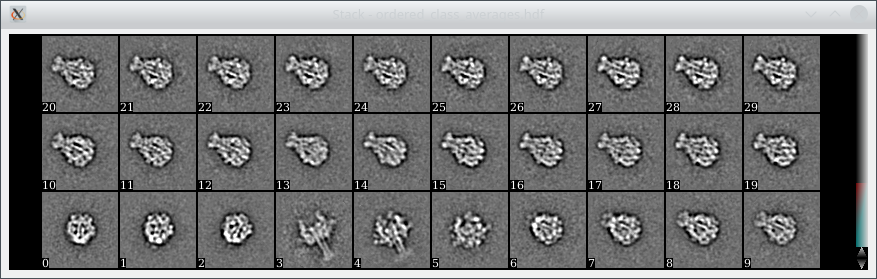 Above: The first thirty class averages out of an overall set of 94 after processing the above data set using GPU ISAC.
Above: The first thirty class averages out of an overall set of 94 after processing the above data set using GPU ISAC.
Usage
Right now GPU ISAC is an excellent tool to screen your data which allows you to:
- Quickly generate 2D class averages.
- Quickly identify suitable parameters for your data set.
- Quickly gauge the quality of your data set before spending time on more costly processing steps.
Ooh, “suitable parameters”sounds great, how do I get those?
Ooh, “suitable parameters”sounds great, how do I get those?
Clustering cryo-EM data is a difficult problem that involves many different parameters and often it is unclear how these impact the resulting 2D class averages. In GPU ISAC the most relevant parameters to fiddle with are:
- Class size: The class (or cluster) size
--img_per_grpin ISAC determines how many particles are taken together in order to construct a new 2D class average. High values will mean cleaner averages, but might also lump together particles that should be sorted into different classes. If you are using GPU ISAC to screen a set of 20,000 to 40,000 particles, then '100' particles per class are a good starting value. Further, the minimun size of each class--minimum_grp_sizeshould be around 60% of set class size. - Threshold error: The
--thld_errparameter determines how similar subsequently produced averages have to be in order to be considered stable enough. A value of0.7is very stringent, while1.4is less so, and you should not need a higher value than2.4.
Since GPU ISAC processes small stacks of about 10,000 to 20,000 particles fairly quickly, you can try several runs with different values for --img_per_group and --thld_err to see which combination gives you the best results.
Once you are happy with the results, you can use these parameters for a full-sized run of (GPU) ISAC. Good luck! :)
Please note that the original version of ISAC was intended to run on a cluster, where resources like RAM are more plentiful than on a single machine running GPU ISAC. There fore please be aware of the the following limitation of the current version of GPU ISAC:
Running memory check.. ..avl sys mem (RAM): 60030.62 MB / 58.62 GB ..est mem req (raw data): 47265.62 MB / 46.16 GB ..est mem req (downsampled data): 8131.41 MB / 7.94 GB
- Current version: If your available system RAM cannot hold the raw data, then your run will fail.
- Next version: If your available system RAM cannot hold the downsampled data, then your run will fail.
For a quick screening of your data, 20,000 to 40,000 particles are usually already enough to produce quality class averages if the quality of your data set is sufficient.
GPU ISAC output files
GPU ISAC produces a multitude of output files that can be used to analyze the success of running the program, even while it is still ongoing. These include the following:
- Main iteration folders: As GPU ISAC is running, it performs multiple “main iterations” and “generations” that are stored within the output folder structure. New class averages are produced during every iteration / generation and can be looked at during runtime without having to wait for the overall process to conclude. This can help to quickly gauge the quality of a data set. Check
path/to/output/mainXXX/generationYYYfor the.hdffiles to that contain any newly produced class averages. - In both the main iteration folders and the base output folder you will find
processed_images.txtfiles. These contain the indices of all processed particles and can be used to determine how many particles GPU ISAC did account for during classification. - The final averages are stored in
path/to/output/ordered_class_averages.hdf.



